프로그래밍 언어/C++
C++ 클래스 배열 포인터 및 2차원 배열 포인터
ShovelingLife
2022. 9. 1. 11:35
클래스 포인터 배열은 아래와 같다.
#include <iostream>
#include <format>
#define SIZE 3
using namespace std;
class A
{
int mVal = 0;
public:
// 생성자
A()
{
cout << "생성자 호출" << endl;
}
// 생성자 오버로딩 파라미터 int
A(int Val) : mVal(Val)
{
}
// 소멸자
~A()
{
cout << "소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
void Print()
{
cout << "현재 주소 : " << this << endl;
cout << mVal << endl;
}
};
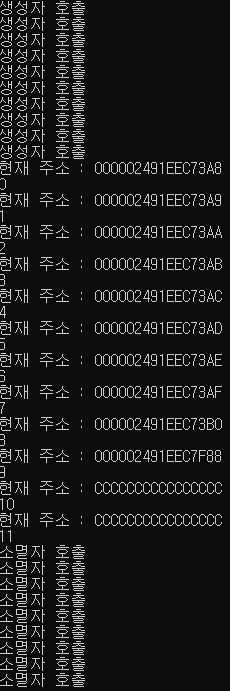
int main()
{
A* arr1[SIZE];
A* arr2 = new A[SIZE];
cout << endl;
// arr1 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
// 여기서 arr1 참조하면 에러 / 할당이 안되어있음
arr1[i] = new A(i + 1);
arr1[i]->Print();
}
cout << "\n arr2 해제" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
// arr2는 이미 전체가 할당 되어있기 때문에 재할당 필요 X
//format("arr2의 주소 : {0}", &arr2 + i);
arr2[i].Print();
}
cout << "\n arr1 해제" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
// 각 원소 해제
delete arr1[i];
}
// new A[]로 해주었기 때문에 해제
cout << "\n arr2 해제" << endl;
delete[] arr2;
return 0;
}
2차원 배열에 대한 포인터는 아래와 같다
#include <iostream>
#include <format>
#define SIZE 3
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
// 생성자
A()
{
cout << "생성자 호출" << endl;
}
// 소멸자
~A()
{
cout << "소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
void Print()
{
static int mVal = 0;
cout << "현재 주소 : " << this << endl;
cout << mVal++ << endl;
}
};
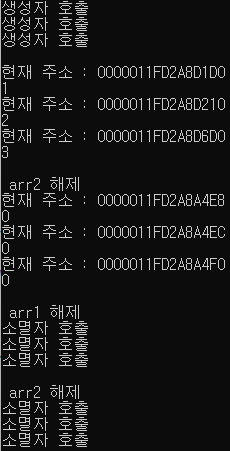
int main()
{
A (*arr1)[SIZE] = new A[SIZE][SIZE];
A* pA = new A[SIZE];
A** arr2 = &pA;
// arr1 출력
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++)
{
arr1[i][j].Print();
}
}
// arr2 출력
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
arr2[i]->Print();
}
// 2차원 배열에 대한 해제
delete[]arr1;
return 0;
}